- info@carbocraft.co.za
- 011 234 0675
- MONDAY-THURSDAY 8:30-4:30 FRIDAYS 8:30-3:30
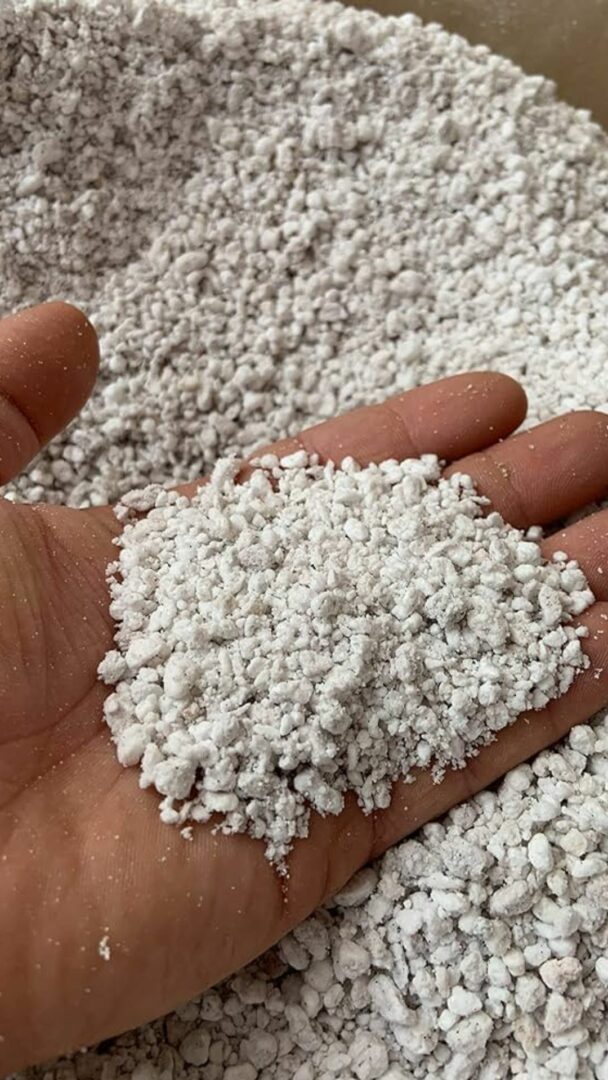
Diatomite & Perlite
CARBOCRAFT is proud to be the exclusive partner and distributor for SHOWA-RTC in Sub-Saharan Africa! Through a close collaboration that spans over ten years, we market and sell a complete line of diatomite products under the brand RADIOLITE® to local food, beverage, and industrial customers. In addition to diatomite, we also supply specialised perlite grades to the local industry under our in-house brand CARBOPERL.

DIATOMITE = DIATOMACEOUS EARTH = KIESELGUHR
Diatomite, also known as diatomaceous earth, and commonly referred to as kieselguhr, is a naturally occurring sedimentary rock composed of fossilized remains of microscopic single-celled algae called diatoms. These diatoms secrete silica-based shells known as frustules, which accumulate over time to form diatomite deposits. Diatomite has a porous and lightweight structure, resembling a fine powder or a soft, chalk-like material.
Chemically, diatomite is primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), which accounts for about 85-95% of its composition. Silica is present in the form of amorphous silica, which means it lacks a distinct crystalline structure. The high percentage of silica contributes to the unique properties of diatomite, such as its high porosity and absorbency.
Diatomite is a highly versatile process aid used in a wide array of diverse applications, including but not limited to the following chief examples:
Diatomite is widely used as a filter medium due to its high porosity and inert nature. It is employed in water purification, food and beverage processing, pharmaceutical production, swimming pools, industrial liquids, and more.
Diatomite is effective as a natural insecticide and pest control agent. It can be used in agricultural settings to control insects like fleas, ticks, ants, and bedbugs, as it dehydrates their exoskeletons upon contact.
Owing to its high porosity, diatomite has excellent absorbent properties. It is utilized in cat litter, spill cleanup products, and as a drying agent in industrial settings. It can absorb moisture and odours efficiently.
Diatomite can be processed into insulating materials like boards or bricks that offer thermal insulation for buildings and industrial applications. It provides excellent heat insulation, fire resistance, and sound absorption properties.
Diatomite is employed in various industrial applications, including additives in paints, plastics, rubber, ceramics, and construction materials. It can enhance properties such as strength, stability, and chemical resistance.
Diatomite is utilized as a soil amendment to improve water retention and nutrient absorption in gardening and crop cultivation. It also helps control pests like slugs and mites.
Diatomite is used in cosmetics, bath powders, toothpaste, and other personal care products due to its absorbency and mild abrasive properties.



What makes diatomite stand out as a super-efficient, natural process aid and what are the attributes that make it so useful in so many different applications?
Here are the key factors that contribute to its exceptional effectiveness:
- Diatomite has a porous structure due to the intricate cell walls of diatoms present in its composition. These microscopic pores allow for effective trapping and retention of particles, impurities, and contaminants during a solid-liquid filtration process. The porosity provides a large surface area for adsorption, making diatomite a highly efficient filter aid.
- Diatomite consists of very fine particles, typically in the range of a few microns. The small particle size ensures a high filtration surface area, allowing for effective removal and physical separation of even sub-micron-sized particulates (<1µm). This makes diatomite an excellent filtration medium for industries requiring fine filtration, such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage processing, and water treatment.
- Diatomite is chemically inert and stable, making it suitable for various applications without adversely affecting the target substance. It does not alter pH, taste, or odour during filtration or processing. Additionally, diatomite is resistant to chemical reactions, making it a reliable choice for filtration in harsh chemical environments.
- Due to its high porosity and adsorption capacity, diatomite can effectively adsorb impurities, contaminants, and smaller particles. This adsorption capability is useful in removing unwanted substances, such as colour, odour, taste, and trace heavy metals, from liquids or gases. Diatomite acts as a molecular sieve that selectively traps and adsorbs specific molecules, significantly enhancing the purification process.
- Diatomite is a naturally occurring resource and is renewable over geological timescales. Its sustainable sourcing and natural origin make it an environmentally friendly choice compared to synthetic alternatives.
NATURAL vs CALCINED vs FLUX-CALCINED
Diatomite is produced from either “freshwater”, “marine”, or “saltwater” diatomaceous earth deposits, with varying levels of purity, specific pore structure, and composition, which are important technical parameters to consider when deciding on a particular diatomite type for a specific application. In addition, we should distinguish between “natural”, “calcined” and “flux-calcined” diatomite, which are typically the three formats in which diatomite is commercially available on the market today:
- Chemically and physically untreated
- Light in colour, ranging from white to light grey or light brown
- Porous and lightweight, low density, typically pH neutral
- Applications: absorbent for cat litter, spill cleanup, and industrial drying agents, natural pesticide in agricultural sector, additive in paints, plastics, rubber, ceramics, construction materials, and personal care products
- Produced by heating natural diatomite at high temperatures (typically around 1000°C)
- Pink in colour, increased porosity, lower bulk density and reduced water absorbency compared to natural diatomite
- Loss of organic matter and compounds results in increased silica content, with enhanced thermal stability and refractory properties
- Applications: insulation in foundries, refractory bricks, and kiln linings, catalyst support and carrier in various chemical processes, lightweight aggregate in concrete and construction materials, filtration medium for hot gases and liquids
- Produced by further heat-treating calcined diatomite (typically around 1700°C) with fluxing agents like soda ash or other alkali compounds
- White in colour, increased crystallinity, creating a more fused and denser structure, leading to a higher melting point and further improved refractory properties compared to natural and calcined diatomite
- Decreased porosity and absorbency, higher bulk density, enhanced abrasiveness and hardness, leading to a higher resistance to chemical reactions and harsh conditions
- Applications: refractory materials for furnaces, crucibles, and industrial refractory applications, insulation and fire resistance solutions in high-temperature processes, abrasives in polishes, toothpaste, and cleaning products, high-density fillers in paints, coatings, and plastics, high-speed filter aid in solid-liquid filtration.
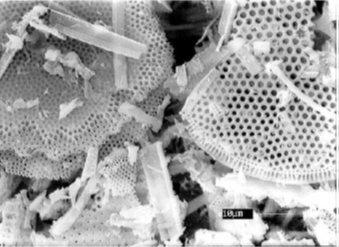
At CARBOCRAFT, we cover the full spectrum of diatomite application fields, through a diverse range of natural, calcined and flux-calcined diatomaceous earth (DE) products, sourced from “freshwater” deposits in China! So, you can rest assured, that we have the right diatomite product for your specific application!
FILTER AID FOR SOLID LIQUID FILTRATION
Although we supply our DE products to various industries, our forte revolves around solid-liquid filtration. Our RADIOLITE® diatomite that we source from our supplier SHOWA-RTC, is manufactured from an ore consisting of the fossilized remains of plankton that lived in freshwater lakes approximately 500 000 years ago. Located in the Jilin Province in China, the SHOWA-RTC production facility that produces our RADIOLITE® products, is strategically positioned in the heart of the rich diatomite deposits of the Changbaishan mountain range.
In association with our esteemed partner SHOWA-RTC and through an excellent long-term collaboration, we can offer our filtration customers the following key advantages that add significant value to their production processes:
- RADIOLITE® diatomite has the highest purity, low iron, and heavy metals (due to inherent freshwater ore characteristics in China).
- RADIOLITE® diatomite delivers an excellent separation efficiency & clarity of filtrate.
- RADIOLITE® diatomite has a high density due to inner porosity resulting in low filter aid usage.
- RADIOLITE® diatomite increases filter productivity by maximising flow rate and prolonging filter cycle times due to high retention capacity.
- RADIOLITE® diatomite improves the spent cake discharge from septum, and results in easy cleaning of the filter.
- RADIOLITE® diatomite is competitively priced per/kg considering “cost-in-use” and leads to improved production and plant economics.
- RADIOLITE® diatomite is produced in China, and China is home to the second biggest DE ore deposit in the world. We can therefore ensure uninterrupted and sustainable supply, with guaranteed supply continuity to all our customers.
- RADIOLITE® diatomite accelerates and streamlines the supply-chain with shorter lead times from China to Sub-Saharan Africa.
- RADIOLITE® diatomite is supplied with full technical support by expertly qualified and skilled filtration technicians, coupled with total plant process optimization initiatives through cooperation with a local solid-liquid filtration partner in South Africa.
- RADIOLITE® diatomite is fully compatible for use with all contemporary filtration equipment and hardware, whether pressure or vacuum systems, including filter presses, pressure leaf filters, plate and frame filters, candle filters, belt stack filters, rotary vacuum drum filters, etc.
- RADIOLITE® diatomite is extremely “operator-friendly” and is renowned for its “ease of slurrying”. It can be applied in a precoat filtration system, or bodyfeed setup, or precoat + bodyfeed system combined.
- RADIOLITE® diatomite is produced in accordance with the highest international and/or Japanese quality standards, and all relevant quality documents and certifications are available on request e.g. ISO, food-grade, food-safety, Kosher, Halal, etc.
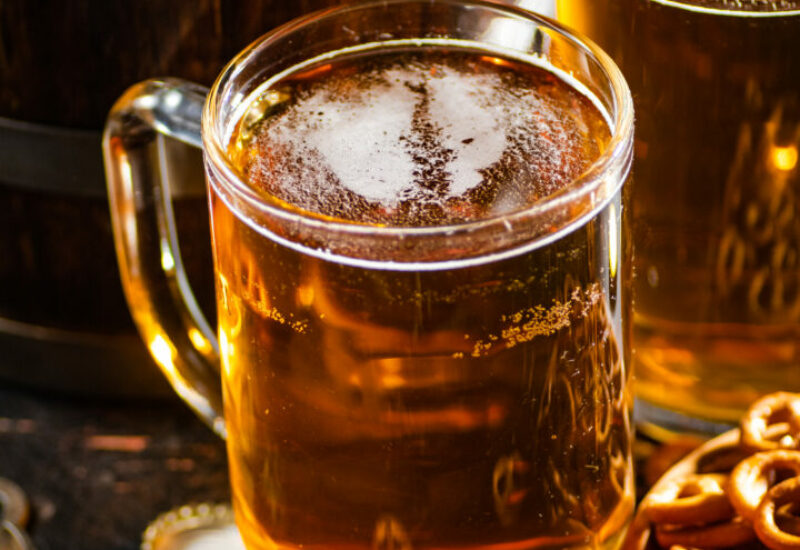
- RADIOLITE® diatomite is used in all known solid-liquid filtration applications, including but not limited to beverage processing (beer, fruit juice, wine), chemical (sulphur, waxes), food processing (edible oil, glucose, sugar), mining, pharmaceutical, swimming pools, water treatment, etc.
Besides the RADIOLITE® diatomite, CARBOCRAFT is the proud supplier of CARBOPERL perlite! Just like diatomite, perlite is similarly a wonderfully versatile and highly useful process aid, and a “naturally occurring” one at that.
Perlite is an amorphous volcanic glass formed from the rapid cooling of molten lava. It contains a high percentage of water bound within its structure, causing it to expand when heated. Chemically, perlite primarily consists of silicon dioxide (SiO2) along with small amounts of other elements like aluminium, potassium, sodium, and iron.
The diverse applications of perlite stem from its unique characteristics, including low density, high porosity, excellent insulation properties, inertness, and accessibility. These properties enable perlite to enhance the performance and efficiency of various products and processes across multiple industries. Here are some of the key applications of perlite:
Perlite is extensively used in horticulture and agriculture as a soil amendment. It improves soil aeration, drainage, and moisture retention while preventing soil compaction. Perlite provides a light and porous medium for healthy root growth and offers insulation against extreme temperatures.
In construction, perlite is utilized as an aggregate in lightweight concrete, plaster, and mortar to enhance thermal and acoustic insulation properties. Perlite insulation is also used to insulate walls, roofs, and cryogenic facilities due to its low thermal conductivity.
Perlite is employed as a filter aid in various industries, including food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment. Its porous structure helps trap fine particles, impurities, and solids, thus achieving high clarity in liquids.
Due to its excellent insulation properties, perlite is used in cryogenic applications for the storage and transportation of liquefied gases. It aids in minimizing heat transfer and maintaining low temperatures for prolonged periods.
Perlite is utilized as a lightweight filler or aggregate in various materials such as plastics, rubber, paints, and coatings. It helps reduce weight, improve thermal properties, and enhance the overall performance of these materials.
Perlite plays a crucial role in oenology, which is the science and study of wine production. It is considered an important process aid in winemaking due to its unique properties. Perlite is widely used as a filter aid in winemaking to clarify and purify the wine. It acts as a filtration medium during the clarification stage, helping to remove unwanted suspended solids, sediment, and turbidity. The porous structure of perlite traps these particles, resulting in a clearer and more visually appealing wine.
Perlite is suitable for both large-scale commercial wineries and small boutique vineyards. It can be used in different filtration systems, such as vacuum drum filters (for lees filtration) or pressure leaf filters (for wine filtration or polishing), commonly referred to as bulk filters in South Africa.
Perlite aids in maintaining the sensory attributes and quality of the wine. By removing unwanted solids and microorganisms, perlite filtration contributes to the stability and consistency of the wine’s colour, aroma, and taste. It helps eliminate undesirable particles that may affect the flavour profile and overall quality of the wine.


